Every ADHD Patient’s Needs Are Different
The FIRST 2.5 mg, 7.5 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg immediate-release
dextroamphetamine tablets available 1.
- Zenzedi® CII (dextroamphetamine sulfate tablets, USP) allows a physician to customize
therapy with precise dosing adjustments
- Zenzedi may help manage symptoms throughout the day with flexible dosing
Available
in SEVEN
incremental
doses!
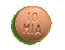
Zenzedi is available in incremental doses ranging from 2.5 mg to 30 mg.
1
Zenzedi provides the FIRST 2.5 mg, 7.5 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg immediate-release
dextroamphetamine tablets available.
A range of dosing options, starting at 2.5 mg, may help manage ADHD symptoms throughout the day.
Zenzedi offers seven dosing strengths differentiated by shape and color.
Zenzedi® (dextroamphetamine sulfate tablets, USP) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant
prescription medicine used for the treatment of:
- A sleep disorder called narcolepsy.
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children 3 to 16 years of age. Zenzedi may
help increase attention and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in people with ADHD.
It is not known if Zenzedi is safe and effective in children under 3 years of age.
Zenzedi is a federally controlled substance (CII) because it contains dextroamphetamine that can be a
target for people who abuse prescription medicines or street drugs. Keep Zenzedi in a safe place to
protect it from theft. Never give your Zenzedi to anyone else because it may cause death or harm them.
Selling or giving away Zenzedi may harm others and is against the law.
WARNING: ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTION
Dextroamphetamine sulfate has a high potential for abuse and misuse, which can lead to the
development of a substance use disorder, including addiction. Misuse and abuse of CNS
stimulants, including dextroamphetamine sulfate, can result in overdose and death, and this risk is
increased with higher doses or unapproved methods of administration, such as snorting or
injection.
Before prescribing dextroamphetamine sulfate, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and
addiction. Educate patients and their families about these risks, proper storage of the drug, and
proper disposal of any unused drug. Throughout dextroamphetamine sulfate treatment, reassess
each patient’s risk of abuse, misuse, and addiction and frequently monitor for signs and symptoms
of abuse, misuse, and addiction.
Do not take Zenzedi if you or your child:
- are allergic to amphetamine products or any of the ingredients in Zenzedi.
- are taking or have taken within the past 14 days, a medicine used to treat depression called a
monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), including the antibiotic linezolid or the intravenous
medicine methylene blue.
What is the most important information I should know about Zenzedi?
Zenzedi may cause serious sides effects, including:
Abuse, misuse, and addiction. Zenzedi has a high potential for abuse and misuse and may lead to
substance use problems, including addiction. Misuse and abuse of Zenzedi, other amphetamine
containing medicines, and methylphenidate containing medicines, can lead to overdose and death. The
risk of overdose and death is increased with higher doses of Zenzedi or when it is used in ways that are
not approved, such as snorting or injection.
- Your healthcare provider should check you or your child’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction
before starting treatment with Zenzedi and will monitor you or your child during treatment.
- Zenzedi may lead to physical dependence after prolonged use, even if taken as directed by your
healthcare provider.
- Do not give Zenzedi to anyone else.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you or your child have ever abused or been dependent on
alcohol, prescription medicines, or street drugs.
Risks for people with serious heart problems: Sudden death has happened in people who have heart
defects or other serious heart disease.
Your healthcare provider should check you or your child carefully for heart problems before starting
treatment with Zenzedi. Tell your healthcare provider if you or your child have any heart problems,
heart disease, or heart defects.
Call your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if
you or your child have any signs of heart problems such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting
during treatment with Zenzedi.
Increased blood pressure and heart rate. Your healthcare provider should check you or your child’s
blood pressure and heart rate regularly during treatment with Zenzedi.
Mental (psychiatric) problems can occur including:
- new or worsening behavior or thought problems
- new or worsening bipolar illness
- new psychotic symptoms (such as hearing voices, or seeing, or believing things that are not real)
or new manic symptoms
Tell your healthcare provider about any mental problems you or your child have, or about a family
history of suicide, bipolar illness, or depression.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you or your child have any new or worsening mental
symptoms or problems during treatment with Zenzedi, especially hearing voices, seeing, or believing
things that are not real, or new manic symptoms.
Before taking Zenzedi, tell your healthcare provider about all of your or your child’s medical
conditions, including if you or your child:
- have heart problems, heart disease, heart defects, or high blood pressure
- have mental problems including psychosis, mania, bipolar illness, or depression, or have a family
history of suicide, bipolar illness, or depression
- have seizures or have had an abnormal brain wave test (EEG)
- have circulation problems in fingers and toes
- have or had repeated movements or sounds (tics) or Tourette’s syndrome, or have a family
history of tics or Tourette’s syndrome
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Zenzedi will harm the unborn baby.
Tell your healthcare provider if you or your child become pregnant during treatment with
Zenzedi.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Zenzedi passes into breast milk. You or your child
should not breastfeed during treatment with Zenzedi. Talk to your healthcare provider about
the best way to feed the baby during treatment with Zenzedi.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines that you or your child take, including
prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Zenzedi and some medicines may interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Sometimes
the doses of other medicines will need to be changed during treatment with Zenzedi. Your healthcare
provider will decide if Zenzedi can be taken with other medicines.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you or your child take:
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- medicines used to treat migraine headaches called
triptans
- lithium
- tramadol
- buspirone
- serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- tricyclic antidepressants
- fentanyl
- tryptophan
- St. John’s Wort
Know the medicines that you or your child take. Keep a list of your or your child’s medicines with you to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you or your child get a new medicine. Do not start any new medicine during treatment with Zenzedi without talking to your healthcare provider first.
What should I avoid while taking Zenzedi?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other potentially dangerous activities until you know how Zenzedi affects you.
What are possible side effects of Zenzedi?
Zenzedi may cause serious side effects, including:
- Slowing of growth (height and weight) in children. Children should have their height and weight checked often during treatment with Zenzedi. Your healthcare provider may stop your child’s Zenzedi treatment if they are not growing or gaining weight as expected.
- Seizures. Your healthcare provider may stop treatment with Zenzedi if you or your child have a
seizure.
- Circulation problems in fingers and toes (peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s
phenomenon). Signs and symptoms may include:
- fingers or toes may feel numb, cool, painful
- fingers or toes may change color from pale, to blue, to red
Tell your healthcare provider if you or your child have numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity
to temperature in your fingers or toes.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you or your child have any signs of unexplained wounds
appearing on fingers or toes during treatment with Zenzedi.
- New or worsening tics or worsening Tourette’s syndrome. Tell your healthcare provider if you or your child get any new or worsening tics or worsening Tourette’s syndrome during treatment with Zenzedi.
- Serotonin syndrome. This problem may happen when Zenzedi is taken with certain other medicines and may be life-threatening. Stop taking Zenzedi and call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you or your child develop any of the following signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome:
- agitation
- fast heartbeat
- flushing
- seizures
- coma
- sweating
- loss of coordination
- confusion
- dizziness
- tremors, stiff muscles, or muscle twitching
- seeing or hearing things that are not real (hallucination)
- changes in blood pressure
- high body temperature (hypothermia)
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
The most common side effects of Zenzedi include:
- fast heartbeat
- decreased appetite
- tremors
- headache
- trouble sleeping
- dizziness
- stomach upset
- weight loss
- dry mouth
These are not all the possible side effects of Zenzedi. Please see Full Prescribing Information for a full
list.
The Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use Zenzedi safely and effectively. Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information for Zenzedi.
To Report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
at 1-800-461-7449, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
PP-ZEN-US-0097